What is Voltage: description; unit, etc
Voltage is one of the basic parameters that describes the electrical conditions in a circuit - and the volt which is the unit of voltage is one of the key parameters for any electrical or electronic circuit.
Voltage Includes:
What is voltage
Electric field
Voltage / potential-divider
Electromotive force
Voltage is one of the fundamental parameters associated with any electrical or electronic circuit. Voltage is seen widely in specifications of a host of electrical items from batteries to radios and light bulbs to shavers, and on top of this it is a key parameter that is measured within circuits as well and used within electronic circuit design calculations.
The unit of voltage or potential difference is the volt and it is widely used in all aspects of electrical and electronic circuits and electronic circuit design. Along with current and resistance the unit of voltage is essential in the design and implementation of any circuit.
The operating voltage of an item of equipment is very important - it is necessary to connect electrical and electronic items to supplies of the correct voltage. Connect a 240 volt light bulb to a 12 volt battery and it will not light up, but connect a small 5V USB device to a 240 volt supply and far too much current will flow and it will burn up and be irreparably damaged.
On top of this, the voltage levels within a circuit give a key to its operation - if the incorrect voltage is present, then it may give an indication of the reason for the malfunction. Also many electrical and electronic components have maximum operating voltages so it is very important to stay within their specifications.
For these and many reasons, electrical voltage is a key parameter and knowing what the voltage is can be a key requirement in any circumstance.
Voltage basics
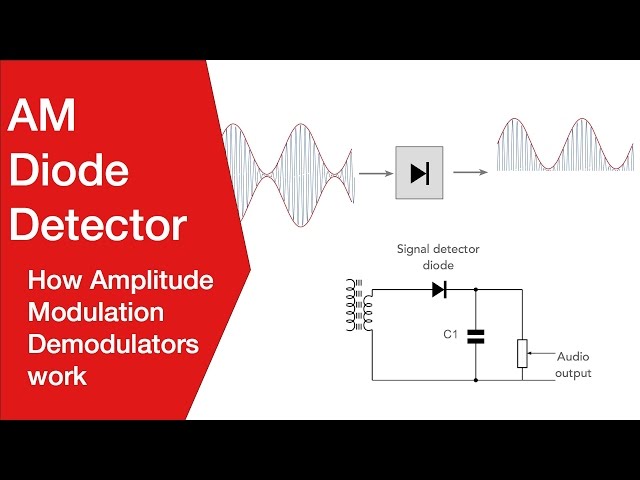
Voltage can be considered as the pressure that forces the charged electrons to flow in an electrical circuit. This flow of electrons is the electrical current that flows
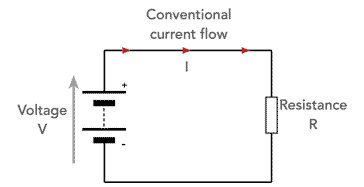
If a positive potential is placed on one end of a conductor, then this will attract that negative charges to it because unlike charges attract. The higher the potential attracting the charges, the greater the attraction and the greater the current flow.

In essence, the voltage is the electrical pressure and it is measured in volts which can be represented by the letter V.
Normally the letter V is used for volts in an equation like Ohm’s law, but occasionally the letter E may be used - this stands for EMF or electro-motive force.
To gain a view of what voltage is and how it affects electrical and electronic circuits, it is often useful as a basic analogy to think of water in a pipe, possibly even the plumbing system in a house. A water tank is placed up high to provide pressure (voltage) to force the water flow (current) through the pipes. The greater the pressure, the higher the water flow.
Alessandro Volta
The unit of voltage or electrical potential is the volt which is named after Alessandro Volta, an Italian physicist who lived between 1745 and 1827.
Note on Alessandro Volta:
Alessandro Volta was one of the pioneers of dynamic electricity. Investigating the basic properties of electricity, he invented the first battery and advanced the understanding of electricity.
Read more about Alessandro Volta.
Potential difference
The electrical potential or voltage is a measure of the electrical pressure available to force the current around a circuit. A useful comparison for these purposes is a simple system containing water such as a water tank with a pipe attached and the water passing through a half open tap. The higher the level of water above the tap, the greater the pressure forcing the water through the pipe and through the half open tap. The greater the water pressure, then the more water that will flow through the system for a given level of resistance in the system.

Similarly with an electrical system, the higher the electric pressure or potential difference across a section of the system, the greater the amount of will pass through the system for a given level of electrical resistance.
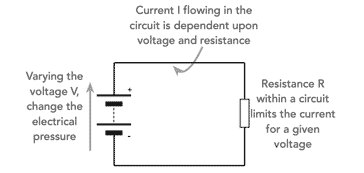
It can be seen that that raising the pressure of water increases the flow. For an electrical circuit raising the electric potential or voltage increases the current flowing.
When looking at the analogy of the water system as an explanation for potential difference, it is worth remembering that it is only a basic analogy, and there are some fundamental differences between the water tank and an electrical circuit, especially in terms of the fact that the electrical circuit is just that, and the water system is not. However it serves well to illustrate the concept of pressure and electric potential in a manner that can be understood.
What is a volt: unit of voltage
The basic unit of voltage is the volt, named after the Italian scientist, Alessandro Volta, who made some early batteries and performed many other experiments with electricity.
The volt definition:
The standard unit of voltage or potential difference and electromotive force in the International System of Units(SI), is formally defined to be the difference of electric potential between two points of a conductor carrying a constant current of one ampere, when the power dissipated between these points is equal to one watt.
To give an idea of the voltages which are likely to be encountered, a CB radio will usually operate from a supply of around 12 volts (12 V). The cells used in domestic batteries have a voltage of around 1.5 volts. Rechargeable Nickel Cadmium cells have a slightly smaller voltage of 1.2 volts, but can normally be used interchangeably with the non-rechargeable types.
In other areas voltages much smaller and much greater than this can be encountered. The signal input to an audio amplifier will be smaller than this, and the voltages will often be measured in millivolts (mV) or thousandths of a volt. The signals at the input to a radio are even smaller than this and will often be measured in microvolts (µV) or millionths of a volt.
At the other extreme much greater voltages may be heard about. The cathode ray tubes in a television or computer monitors require voltages of several kilovolts (kV) or thousands of volts, and even larger voltages of millions of volts or megavolts (MV) may be heard of in conjunction with topics like lightning.
EMF and PD
When dealing with voltages, two terms will often be seen: electromotive force, EMF and potential difference, PD. These terms have many similarities, but also some key and very important differences.
Both EMF and voltage both use the same unit - the volt, but what the terms represent is different.
How to measure voltage
One of the key parameters that needs to be known in any electrical or electronic circuit is the voltage. There are several ways in which voltage measurements can be made, but one of the most common is to use a multimeter. Either analogue or digital multimeters can be used, but these days digital multimeters are most commonly used as they are more accurate and are available for very reasonable prices.
Note on how to measure voltage with a Multimeter:
Voltage is one of the key parameters that needs to be known in any electrical or electronic circuit. Voltage can easily be measured using an analogue or digital multimeter where accurate readings can be taken very easily.
Read more about how to measure voltage.
Voltage is one of the three main electrical units along with current and resistance. Voltage is key to the electronic circuit design process as well as that of any electrical circuits. Accordingly it is used in virtually all design processes and a parameter which is associated with very many electrical and electronic components.
 Written by Ian Poole .
Written by Ian Poole .
Experienced electronics engineer and author.
More Basic Electronics Concepts & Tutorials:
Voltage
Current
Power
Resistance
Capacitance
Inductance
Transformers
Decibel, dB
Kirchoff's Laws
Q, quality factor
RF noise
Waveforms
Return to Basic Electronics Concepts menu . . .