Solar Panel Technology for PV Energy Generation
Solar panels are used as the basis for any photovoltaic or solar electricity generation systems where they are the item used for converting solar energy to electrical energy.
Solar Energy Generation Includes:
Solar electricity generation
Solar panels
Monocrystalline vs polycrystalline solar panels
When looking at any solar electrical generation system, the solar panels are the key element.
The solar panels are based on solar cell technology, an effect that has been known for many years, but only developed to be used in relatively recent times.
The performance of solar panels has improved considerably in recent years as the need for solar energy has grown, and the number of solar power systems has increased.

Solar cell technology is the basis for solar panels
Solar panels use solar cell technology. They use solar cells of photovoltaic semiconductor diodes as the basis for their operation.
Solar panels are made up from a number of solar cells - they are effectively a form of semiconductor diode that generates a current when light impacts on to the diode junction.
As solar energy in the form of light falls on the semiconductor diode junction it releases electrons and these form the electric current providing the power that can be used in electrical systems. Effectively they convert the solar energy into electrical energy.
Note on the Solar Cell or Photovoltaic Diode:
Solar cells are widely used to convert solar energy into electrical energy for everything from small solar cells in electronic calculators to large solar panels used for electricity generating systems.
Read more about Solar Cell / Photovoltaic Diode.
Monocrystalline and poly crystalline solar panels
Although there are many specifications and figures associated with solar panels, one of the key aspects is whether they are monocrystalline or polycrystalline.
These are the two main types of solar panel, and for any solar electricity generation system, a choice will need to be made regarding which type to use. Monocrystalline tend to be more expensive but offer a higher efficiency and longer lifetime. Polycrystalline ones are less expensive, but provide a lower level of performance.
Practical aspects of solar panels: construction, sizes, etc
The construction of a solar panel needs to be such that it can withstand the rigours of use externally. It needs no be resistant to wind, rain and long term exposure to UV radiation, etc. On top of this it needs to be resilient when handled and transported as well as being easy to mount into a roof or other system - external fixing features must be robust and reliable.
Most solar panels deliver maximum power levels of around 200 - 350W per panel. This is dependent upon the actual size of the panel and the technology used, monocrystalline, polycrystalline, etc. It is worth noting that these figures will only be achieved under full illumination at the optimum angle. This means that for most of the day, a lower solar power level will be generated.
It is difficult to give exact figures as there are very many products available, but as a guide, a typical solar panel will provide between about 200 - 350 Watts and it will generally have dimensions in the region of 1.6 metres (63 inches) x 1 metre (39 inches) and a thickness of around 45mm (1.8 inches). They can also weight between 20 - 25kg ((40 - 50 lbs). These are only very rough guidelines as many different products have very different dimensions and weights.
The weights give an indication about the robustness of their construction.
The panels don't just consist of a solar cell, they need to be properly mounted and protected. Typically a solar panel consists of the solar cells themselves. Directly above and below is an encapsulation EVA film layer.
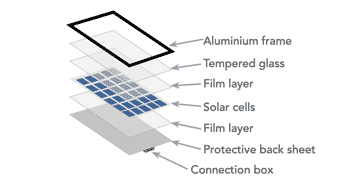
For the underside of the panel, there is a back sheet, but above the solar panels and the EVA film layer is a sheet of tempered glass and finally an aluminium frame holds everything together. A junction box is included on the bottom of the assembly to enable easy connection.
Practical solar panel installation aspects
When considering where to locate solar panels there are several aspects to consider to ensure the optimum solar energy conversion. By locating the panels in the best way, it is possible to ensure that the most solar power is obtained.
Orientation of roof or angle of the panels: In order to be able the maximum amount of solar energy to electrical energy, the panels must be located on a roof or other structure that faces towards the sun. For the northern hemisphere this should be a south facing roof or other structure.
Potential shade: If the solar panels are to be located on a roof, there may not be a huge amount of choice in exactly where they can be located. If possible the solar panels should be located sot hat they do not get any shade from objects like trees, chimneys and the like. This will ensure they receive the maximum amount of solar energy to convert into electrical energy.
Roof angle: When mounting solar panels on a roof, the roof angle can have an impact upon the amount of solar energy that is captured. Ideally the sun should be at right angles to the panels for as long as possible. Typically there is an optimum angle so that as the Sun rises in the sky, so the level of solar power or radiation it receives rises and the resulting energy generation increases.
For any given location, there is an optimum angle for a fixed array of solar panels. For example in London England the optimum angle is 51°, whereas further north in Aberdeen Scotland it is 57°
The best answer is to have adjustable solar panels where the angle can be adjusted for the maximum solar radiation to give the maximum amount of solar power. However this is not really an option for most installations.
Number of panels & their size: The more panels that can be placed on a roof the greater the amount of solar energy that can be captured. However there are limitations of area available and the weight that can be supported. When installing solar panels, which can be quite heavy, it is always best to have a survey done to ensure the roof can carry the proposed weight.
When selecting the panels it is necessary to look at the size of the solar panels, the fixing racking, the weight, and the available area. Also consider the difference between monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels to get the required power from the panels within the available area. One of the many advantages of monocrystalline solar panels is that they give a higher output for a given area when compared to polycrystalline ones. However monocrystalline ones are more expensive.
Solar cell and solar panel technology is moving forward as the requirements for solar panels increase. Reports indicate that the market for them is growing by a rate of at least 20% per year with the increased requirements for solar power. With such interest in solar energy, the development of solar panel technology will move forward, and improvements will be seen in the future.
 Written by Ian Poole .
Written by Ian Poole .
Experienced electronics engineer and author.
More Eco / Green Engineering Topics:
Smart meter technology
Solar electricity generation
Smart grid
Home energy saving technology
LED lights
Energy saving guidelines
Return to Eco / Green Engineering menu . . .


